The term Sexism, was coined in mid-20th century, it refers to prejudice towards or hatred of, either sex, or the appliance of stereotypes of masculinity with regards to men, or of femininity with regards to women.
Sexism in India refers to the attitude or belief that one sex or gender is inferior to, less valuable or less competent than the other. Discrimination and cruelty against women is widespread, and sexual harassment at offices and illiteracy continue to be recognized as main problems. Some men protest that the government is discriminating against men through the use of excessively belligerent laws designed to defend women and sexism in India, and by added socio-economic methods they favor females, like higher benefits and lower taxes. These benefits are deemed necessary to equalize the continuing as well as historic wealth imbalance between both genders.
Few facts about sexism in India:
1. The constitution of India includes a clause assuring the right of freedom and equality from sexual discrimination.
2. Women have 33% reservation in municipal and panchayats elections. The procedure of extending it to the Indian parliament is also ongoing.
3. Domestic violence against women is a big problem in India.
4. A report by the Indian Communist Party staes that between January and April in the state of Bihar there were 159 kidnappings of women, 221 rapes, 51 cases of murder and rape and 144 cases of dowry homicide.
5. Studies show that up to 70% of married women between the age of 15 to 49 are victims sexism in India in the form of coerced sex or beatings.

6. Eve teasing is another category of sexism in India, which involves sexual molestation or harassment of women by men.
7. Half of the crimes against women are related to harassment and molestation at the place of work.
8. The Supreme Court of India took a landmark judgment in 1997, against sexual harassment of women in their place of work. The Court also gave a detailed course of action for impediment and redressal of grievances.
9. The number of born and surviving girl child in India is drastically less compared to the number of boys, caused by deliberate disregard for girl child and leaving them to die and a large number of female foetuses being aborted.

10. The standard ratio of births is supposed to be for every 1000 boys there should be 950 girls, yet in most regions it is found to be as low as 300. The low sex ratio is caused by sex-selective abortions and female infanticides.
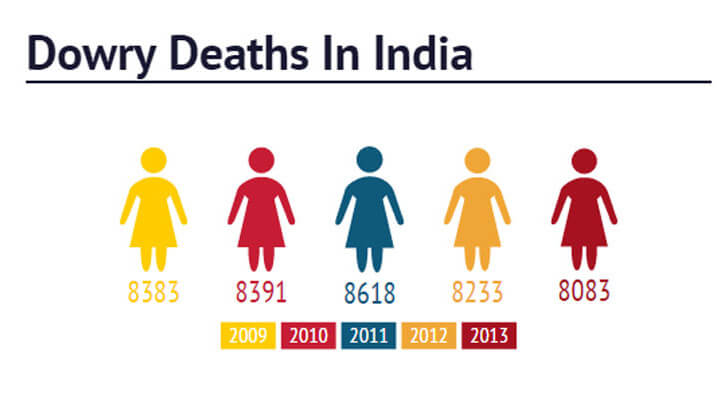
11. Another form of sexism in India is dowry deaths. The Government of India passed Dowry Prohibition Act in 1961, which explicitly makes the dowry demands unlawful in wedding arrangements.
12. The Dowry Prohibition rules were laid down in 1985. However, these rules are scarcely enforced.
13. A 1997 study proves that 5,000 women as a minimum die every year because of dowry deaths, and no less than a dozen die every day in the so called ‘kitchen fires’ which are often suspected to be intentional.
14. Sexism in India is gradually rising, and the major contributing factor in the rise of this issue is female literacy rate which is much lower for Indian women as compared to men.
15. As per 1997‘s National Sample Survey Data, the states of Mizoram and Kerala are the only ones that have come within the reach of global female literacy rates.
16. The main obstruction to female edification in India is insufficient school facilities (like sanitary facilities), scarcity of female teachers and the prevalent gender bias in curriculum.
17. Sexism in India can also be seen in armed forces where women are not permitted to have combat roles.